Organic Chemistry
Introduction
Organic chemistry, also known as “carbon chemistry”, is chemistry involving organic — or “carbon-based” — molecules. All life on Earth can be considered an expression of complex carbon chemistry. However, since lots of non-living things are carbon-based as well, organic chemistry isn't merely limited to biochemistry. Organic chemistry also deals with polymers, petroleum products, and much more.
Organic Molecules
See Organic Molecules.
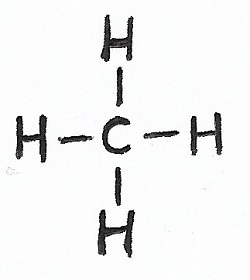 Methane |
|
 Ethene |
|
 Ethyne |
|
|
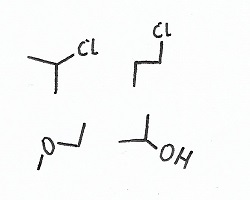
Regiochemistry — |
|
|
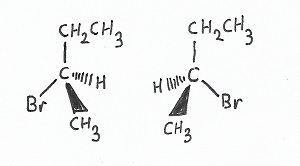
Stereochemistry — |
|
Conformation
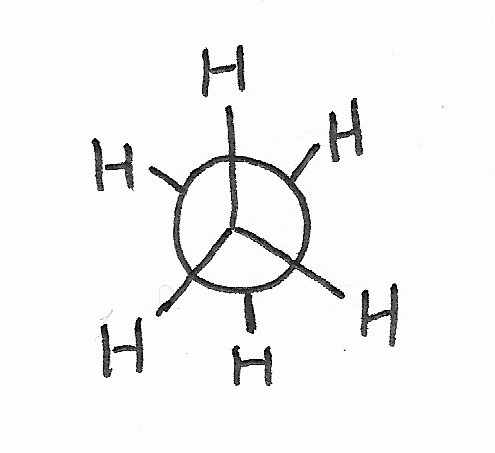 |
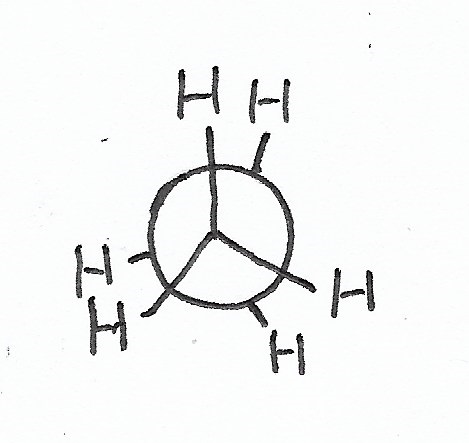
Staggered Conformation — is the stablest conformation for C-C bonds. |
 |
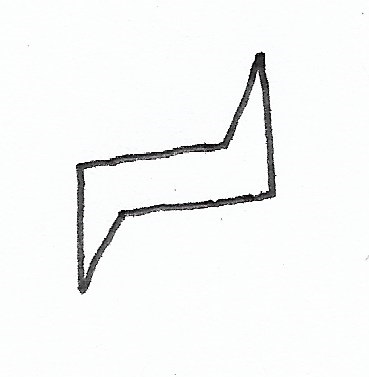
Eclipsed Conformation — causes the most steric hindrance. |
 |
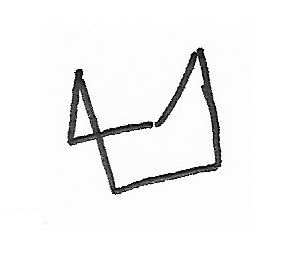
Chair Conformation — the stablest conformation for cyclohexane rings. |
 |
Boat Conformation — |
Ionization & Formal Charge
 |
Carbocation — a carbon with only three bonds and a positive formal charge. |
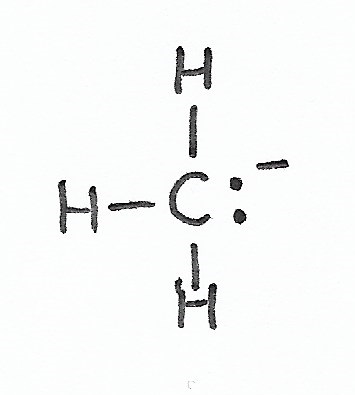 |
Carbanion — has one lone pair of valence electrons and a negative formal charge. |
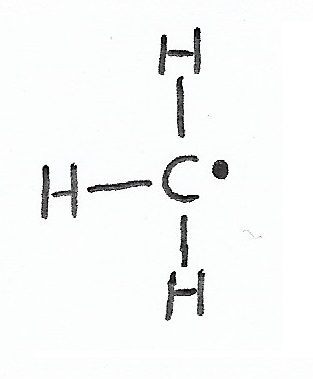 |
Free Radical — have a single, unpaired valence electron and a formal charge of zero. |
Acids & Bases
For more information, see acids & bases.
 |
Acid Disassociation Constant [Ka] — stronger acids have a larger Ka value. |
|
pKa — negative log of the acid disassociation constant. |
|
|
Proton Concentration [pH] — a lower pH value indicates greater acidity, while a higher pH value indicates great basicity. |
|
|
Equilibrium Constant [Keq] — |
Table of Reactions
| Reaction Type | Reagents | Products | ||||
| Addition | Polar | Electrophilic | Dihalo addition | |||
| Hydrohalogenation | ||||||
| Hydrogenation | ||||||
| Hydration | Hydroboration-Oxidation | Alkenes | Alcohols | |||
| Mukaiyama’s Hydration | ||||||
| Oxymercuration | ||||||
| Nucleophilic Addition | ||||||
| Non-Polar | Free-radical | |||||
| Cycloaddition | ||||||
| Substitution | Electrophilic | Aromatic | ||||
| Aliphatic | Nitrosation | |||||
| Ketone halogenation | ||||||
| Keto-enol tautomerism | ||||||
| Nucleophilic | Unimolecular [SN1] | |||||
| Bimolecular [SN2] | ||||||
| Aromatic [SNAr] | ||||||
| Internal [SNI] | ||||||
| Elimination | Unimolecular [E1] | |||||
| Bimolecular [E2] | ||||||
Regiochemistry
Markovnikov
Stereochemistry
Anti adddition
Syn addition
Erata
Check out this pure HTML periodic table of elements.

