Electrophilic Addition
Overview
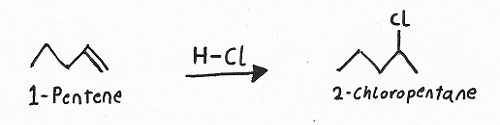
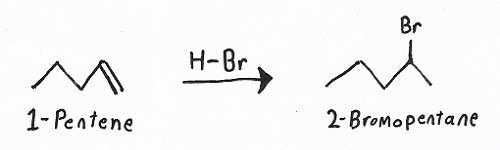
Reagents: — HX (HBr, HCl, or HI), H2SO4 + H2O, or Br2 or Cl2 in CCl4.
Products: — Haloalkanes / alkyl halides, alcohols, or 1,2-dihalides.
Table of Reactions
| Reaction Type | Reagents | Products | ||||
| Addition | Polar | Electrophilic | Dihalo addition | |||
| Hydrohalogenation | ||||||
| Hydrogenation | ||||||
| Hydration | Hydroboration-Oxidation | Alkenes | Alcohols | |||
| Mukaiyama’s Hydration | ||||||
| Oxymercuration | ||||||
| Nucleophilic Addition | ||||||
| Non-Polar | Free-radical | |||||
| Cycloaddition | ||||||
| Substitution | Electrophilic | Aromatic | ||||
| Aliphatic | Nitrosation | |||||
| Ketone halogenation | ||||||
| Keto-enol tautomerism | ||||||
| Nucleophilic | Unimolecular [SN1] | |||||
| Bimolecular [SN2] | ||||||
| Aromatic [SNAr] | ||||||
| Internal [SNI] | ||||||
| Elimination | Unimolecular [E1] | |||||
| Bimolecular [E2] | ||||||
Addition Reactions
Hydroboration/Oxidation
Reagents: — BH3/THF followed by NaOH/H2O2.
Products: — Hydroboration/Oxidation always produces alcohols.
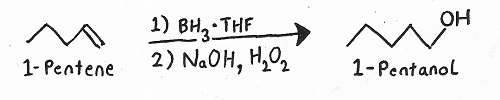
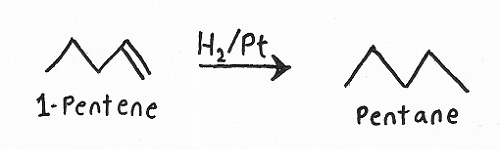
Hydrogenation
Regiochemistry
Markovnikov
Anti-Markovnikov
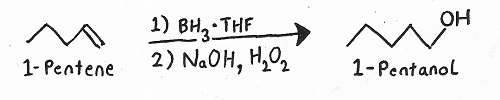
Stereochemistry
Anti adddition
Syn addition
Erata
Check out this pure HTML periodic table of elements.

